Backup using /scripts/pkgacct and Restoring
Log-in to the Server as root
Grep Domain to get the username
--------------------------------------------
[root@server ~]$ grep domainname /etc/userdomains
example
[root@server ~]$ /scripts/pkgacct example
After Full Backup move it to user's public_html so that user can download it
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[root@server ~]$ cp cpmove-example.tar.gz /home/example/www/
Give Appropriate Permissions and Assign Ownership
-------------------------------------------------------------------
[root@server ~]$ cd /home/example/www
[root@server www]$ chmod 755 cpmove-example.tar.gz
[root@server www]$ chown example.example cpmove-example.tar.gz
RESTORING PACKAGE
---------------------------
[root@server ~]$ /scripts/restorepkg example
DONE !
.htaccess redirect rules
.htaccess redirect rules
Use below mentioned .htaccess rules as per your requirment.
#// This allows you to redirect your entire website to any other domain
Redirect 301 / http://example.com
#// This allows you to redirect your entire website to any other domain
Redirect 302 / http://mt-example.com/
#// This allows you to redirect index.html to a specific subfolder
Redirect /index.html http://example.com/newdirectory/
#// Redirect old file path to new file path
Redirect /olddirectory/oldfile.html http://example.com/newdirectory/newfile.html
#// Provide Specific Index Page (Set the default handler)
DirectoryIndex index.html
Hpe this will help you lot :)
Change main domain to subfolder
Change main domain to subfolder
Use below mentiond .htaccess rule in your document root in order to redirect your main domain to subdomain without changing the url.
=============================================================
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^(www.)?main\-domain.com$ [NC]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} !^/sub\-folder/
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ /sub-folder/$1
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^(www.)?main\-domain.com$ [NC]
RewriteRule ^(/)?$ sub-folder/index.php [L]
============================================================
WEBSERVER
PACKAGES NEEDED FOR CONFIGURATION
httpd
IF THE PACKAGES ARE NOT AVAILABLE INSTALL THROUGH YUM INSTALLER
yum install httpd
THE MAIN CONFIGURATION CAN BE EDITED AS FOLLOWS
vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
shift+g==>
<VirtualHost 192.168.0.X:80>
DocumentRoot /var/www/html
ServerName stationX.example.com
</VirtualHost>
httpd
IF THE PACKAGES ARE NOT AVAILABLE INSTALL THROUGH YUM INSTALLER
yum install httpd
THE MAIN CONFIGURATION CAN BE EDITED AS FOLLOWS
vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
shift+g==>
<VirtualHost 192.168.0.X:80>
DocumentRoot /var/www/html
ServerName stationX.example.com
</VirtualHost>
PHP handlers for Apache
In this article, I'll explain about the PHP Handlers on Apache Web server which are widely discussed in the context of Hosting Industry. There are two ways to configure Apache to use PHP :
(1) Configure Apache to load the PHP interpreter as an Apache module (DSO)
(2) Configure Apache to run the PHP interpreter as a CGI binary (CGI)
PHP Handlers
A handler is a piece of code built into Apache that performs certain actions when a file with a particular MIME or handler type is called. PHP handlers are the programs that interpret the PHP code in your web application and process it to be sent as HTML (or another static format which the web browser understands) by your web server. None of the major web servers available today can handle PHP by themselves which is why they need another program to do it for them. This program, known as a PHP handler takes all the PHP code and generates the output which is then sent to the web server which forwards it on to the user upon request. Currently there are Four major PHP handlers available on Apache. They are CGI, DSO, suPHP, & FastCGI. Each handler delivers the libraries through different files and implementations. Each file and implementation affects Apache’s performance, because it determines how Apache serves PHP. I will be explaining these handlers one by one from here.
Addon Domain
Addon domain?
The addon domain option within cPanel allows you to host multiple websites/domains under a single cPanel account. You can give e-mail accounts and forwarders for domains added. All analytics are calculated separately.
The addon domain option within cPanel allows you to host multiple websites/domains under a single cPanel account. You can give e-mail accounts and forwarders for domains added. All analytics are calculated separately.
To create a second domain in your hosting account, please do the following:
Login to your cPanel account and click Addon Domains, under Domains tab. There are Four fields cPanel asks for when creating an Addon Domain.
1. New Domain name
2. Subdomain/FTP username.
3. Document root.
4. Password.
How to Remove an Addon Domain from cPanel
If you have an Addon Domain set up and would like delete it, please do the following:
- Login to your cPanel and click Addon Domains.
- At the bottom, under Actions, click Remove.
Please note removing the addon domain only removes the domain from the DNS and server configuration. Your files and databases are not deleted or affected by removing the addon domain.
I hope this post will help you lot.
.htaccess error reporting (PHP)
Ihave added below mentioned line in .htaccess file inorder to display PHP error.
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
php_flag html_errors on
In some case you may face some errors like "Internal server error" while adding above lines. In such cases use below mentioned lines in your .htaccess file.
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
php_flag html_errors on
php_flag log_errors on
php_value error_log /home/path/public_html/domain/PHP_errors.log
Hope this will help you :)
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
php_flag html_errors on
In some case you may face some errors like "Internal server error" while adding above lines. In such cases use below mentioned lines in your .htaccess file.
php_flag display_startup_errors on
php_flag display_errors on
php_flag html_errors on
php_flag log_errors on
php_value error_log /home/path/public_html/domain/PHP_errors.log
Hope this will help you :)
List of services and corresponding runlevels
Run levels
================
On the console, you use the chkconfig tool list and specify which services to run at different
runlevels.
List of services and corresponding runlevels
[root@server ~]# chkconfig --list
acpi-support 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
acpid 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
alsa-restore 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
alsa-store 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
anacron 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
apparmor 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off S:on
apport 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
atd 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
autofs 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
avahi-daemon 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
bind9 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off
binfmt-support 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
bluetooth 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
bootlogd 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off
brltty 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off S:on
Apache Semaphore issue
Semaphore issues
This
is one of the rarest conditions which I came across. The webserver
failed to load with following error messages in the server log file. The
server had fairly good uptime and was a busy server.
============================================================
[emerg] (28)No space left on device: Couldn't create accept lock
[notice] suEXEC mechanism enabled (wrapper: /usr/sbin/suexec)
[notice] Digest: generating secret for digest authentication ...
[notice] Digest: done
[warn] pid file /etc/httpd/run/httpd.pid overwritten -- Unclean shutdown of previous Apache run?
[emerg] (28)No space left on device: Couldn't create accept lock |
Apache service issue - Module issues
Module issues
Apache may experience issues to load apache modules
configured . The error log will contain the information indicating the
issue. In such cases, make sure the .so file of the module is present
in the correct location and it is accessible. If the location is correct
check whether the module has any issues. You can check it using the
command “ldd”
A sample output would look like this
root@redhat003 [/usr/local/apache/modules]# ls./ httpd.exp ../ mod_hostinglimits.so* mod_security2.so
Apache service issue - Unable to bind to port
Unable to bind to port
The webserver will fail to bind to the concerned port i.e. 80 if it is open by another process. In such cases, we need to identify the process which occupies the port and need to terminate it.The following command will show the existing connections to port 80
#
The webserver will fail to bind to the concerned port i.e. 80 if it is open by another process. In such cases, we need to identify the process which occupies the port and need to terminate it.The following command will show the existing connections to port 80
#
netstat -an | grep \\.80
orYou can identify the apache process using the command as well
# pgrep httpd
orThe process associated with the port number using the following command:
#lsof -i tcp:80
Apache service issue Log file size
Log file size
Older kernal versions may not be capable of handling files more than 2 GB. This creates issue for apache if the size of error_log exceeds 2 GB. In such cases, simply clearing the log file alone fix the issue.
# : > /usr/local/apache/logs/error_logWhitelist Mod_security rules for a CPanel account
Preface:
Sometimes you may arise an issue like this. When a client tries to install IFrames he gots the following error
"you don't have permission to access /e107_admin/cpage.php on this server"
This issue arises due to this installtion is blocked by a mod_security rule
Recover the issue
First you’ll need to get the Rule ID number. You can find these either in the apache error log (grep for your IP) or if you have CSF installed and keep getting your IP blocked, check /etc/csf/csf.deny to see if its listing the mod_security rule that you were blocked from.
ie
#grep <ip> /usr/local/apache/logs/error_log
or
#grep <ip> /etc/csf/csf.deny
From here you will get the application ID
Once you have the rule’s id number, you will need to create the following file
vi /usr/local/apache/conf/userdata/std/2/USER/<domain.com>/<anything>.conf
For example
vi /usr/local/apache/conf/userdata/std/2/USER/example.com/modsec.conf
Now open the .conf file and add the below mentioned lines in it.
<IfModule mod_security2.c>
SecRuleRemoveById <NUMBER>
</IfModule>
Be sure to replace <NUMBER> with the Rule ID number of the mod_security rule you need to whitelist. Save the file, and then run the following commands, replacing <CPANEL USER> with the actual cpanel user name.
/scripts/ensure_vhost_includes --user=<CPANEL USER>
/usr/local/cpanel/bin/apache_conf_distiller --update
/usr/local/cpanel/bin/build_apache_conf
:)
cPanel Shell commands
Restart chkservd:
/etc/init.d/chkservd restart
Tail Apache log:
tail -f /usr/local/apache/logs/error_log
Updates the cpanel server software:
/scripts/upcp
Reinstalls exim:
/scripts/exim4
View traffic or if you think a site is being DDoS:
cd /usr/local/apache/domlogs
tail -f targetsite.com
Correct bandwidth issues
/scripts/cleanbw
Useful commands
Useful Commands for checking the domains
1:#traceroute domain.com
2:#whois domain.com
3:#dig domain.com
4:#ping domain.com
File permissions in cPanel accounts
Please use below mentioned files for your account
Permissions
/home/user 711
/home/user/public_html 750
public_html/directory 755
public_html/file 644
Command to find the hacked files
You can search the hacked files using the below mentioned command
#grep -ril <hack content> ./*
For example
#grep -ril 'Hacked By Sizzling Soul' ./*
Wordpress Blank page occuring when clicking on Permalinks
Officially, Permalinks are the permanent URLs to your individual weblog posts, as well as categories and other lists of weblog postings. A permalink is what another weblogger will use to link to your article (or section), or how you might send a link to your story in an e-mail message. The URL to each post should be permanent, and never change — hence permalink.
Permalinks would help us to retrieve an article from a huge collection and its the most important significance of it.
In this article, I'm going to describe how an issue with the Blank Permalinks page can be resolved
Issue
The Permalinks page in Wordpress Administration panel appears to be Blank
Whereas it should be show more options
Mysql Connection
The below mentioned command is used for the mysql connection test.
1. Touch a php file for example
connection.php
2. Coppy paste below mentioned code in that file
1. Touch a php file for example
connection.php
2. Coppy paste below mentioned code in that file
Traceroute
You can use below steps to take the traceroute results from different operating systems.
In Windows,
Start > Programs > Accessories > Command Prompt.
c:\> tracert <domain.com>
Linux:
get into a terminal and execute the command as given below
$traceroute <domain.com>
MAC
These steps were created using Mac OS X. For earlier operating systems, you will need to download and use a third party program.
1. From your hard-drive, open the Applications folder, and click to open the Utilities folder.
2. Double-click Terminal.
3.Type traceroute followed by your domain name, and hit Enter.
Iostat
Iostat
iostat (input/output statistics) an utility that reports Central Processing Unit (CPU) statistics and input/output statistics for devices and partitions. The iostat command is used for monitoring system input/output device performance. This is quite handy to identify which partition is being heavily used and if any HW issues exists. The details regarding the various parameters will make this article quite confusing. So I am focusing on the values which needs to be monitored during a suspected server issue.
# iostat -x
As you can see from the result the first part explains the IO activities for the cpu. You can get the CPU performance alone using the following command-line.
How to clear /temp
You can use below mentioned commands
find /tmp -size +2M -mtime +2 -exec rm {} \;
Removes all files greater than 2 MB size that was last modified before 48 hours
Remove Sess files
find . -type f -name "FILE-TO-FIND" -exec rm -f {} \;find /tmp -type f -name "sess_*" -exec rm -f {} \;
use this along with mtime parameter only or this will never end
Socket and Port
Socket vs Port
In the context of computer networking, a socket is an end point of a bidirectional communication that occurs in a network that is based on the internet protocol. Sockets will distribute the data packets that are coming through the communication channel to the correct application. This is done using the information such as IP address and port number. In general a (software) port is a logical data connection that can be used to exchange data. On the internet TCP and UDP ports are used to exchange data between computers and these are the most widely used ports.
Basic cPanel Details
Ports
Webmail - 2095
whm - 2086
cPanel - 2082
grep domain.com /etc/userdomains
grep example.com /etc/userdomains
The primary domain of a user , is specified in the file /etc/trueuserdomains
Packages -
user details
/var/cPanel/users/<username>
If the account is not a resold one then the owner will be either "root" or the one specified by the admin.
The packages are placed within the folder /var/cPanel/packages
/var/cPanel/features:
Disk space script fixes it normally: /scripts/fixquotas
exiqgrep & exigrep
exiqgrep & exigrep
exigrep searches the log, while exiqgrep is exim queue grep. See the table which has the link to the documentation as well.
52.2 exiqgrep grep the queue
52.3 exiqsumm summarize the queue
52.4 exigrep grep search the main log
Exiqgrep Options & Usages
Options What is the option for Usage
-i list the message IDs exiqgrep -i
-z show frozen messages exiqgrep -z
-x show unfrozen messages exiqgrep -x
-f match the sender address exiqgrep -f beserk2@server1.beserk.com.au
-r match the recipient address exiqgrep -r update_profile@westpac.com.au
-c count the matching results exiqgrep -c -r update_profile@westpac.com.au
-o older than a number of seconds exiqgrep -o 43000
-y younger than a number of seconds / to get the latest emails exiqgrep -y 3600
Shell
The word Shell is an application / binary / program in Linux/ Unix machines.
Details
The main purpose of a shell (the program) is to act as an interface between the Operating System's Kernel and the user. Basically when you type ls command in the shell programs like /bin/bash, ksh, sh, csh or tcsh, shell or those programs are taking the keyboard inputs of `ls` and when you type an ‘Enter’ it passes `ls` command to the shell. The shell tries to interpret those keystrokes as commands.
The shell applies its built-in rules to figure out that you want to run the executable command in the file /bin/ls. It makes a system call asking the kernel to start /bin/ls as a new child process and give it access to the screen and keyboard through the kernel. Then the shell goes to sleep, waiting for ls to finish.
When /bin/ls is done, it tells the kernel it's finished by issuing an exit system call. The kernel then wakes up the shell and tells it it can continue running. The shell issues another prompt and waits for another line of input.
It's called a shell because it wraps around and hides the operating system kernel.
Other usages of word shell in an Unix box
The /etc/shells file contains a list of login shells on the system. Applications use this file to determine whether a shell is valid
=======================================================
sarath@sage3:~$ cat /etc/shells
# /etc/shells: valid login shells
/bin/sh
/bin/dash
/bin/bash
/bin/rbash
/usr/bin/screen
======================================================
For more details, check References
References
http://www.iitk.ac.in/LDP/HOWTO/Unix-and-Internet-Fundamentals-HOWTO/running-programs.html
http://www.lancs.ac.uk/~tipper/writing/luui/html/unix-intro007.html
Exim Commands
1. To check the number of emails present in the queue:
# exim -bpc
2. To check the emails present in the queue with the mail id and sender ID:
# exim -bp
# exim -bp | less
3. To view the header of a particular email using mail ID:
# exim -MvH mail_id
4. To view the body of a particular email using mail ID:
# exim -Mvb mail_id
5. To view a message's logs:
# exim -Mvl mail_id
# exim -bpc
2. To check the emails present in the queue with the mail id and sender ID:
# exim -bp
# exim -bp | less
3. To view the header of a particular email using mail ID:
# exim -MvH mail_id
4. To view the body of a particular email using mail ID:
# exim -Mvb mail_id
5. To view a message's logs:
# exim -Mvl mail_id
How to create CSR for SSL Installation
SSL means Secure Sockets Layer. It is a technology that the communications between the user and the web server go through in a encrypted format. It helps to prevent hack attacks from outside. You see a padlock icon when you use a web page that is protected by SSL, that assures you that the page is secure.
Please note
For SSL installation the account require dedicated IP and a valid SSL Certificate
Steps to create CSR from WHM
1.Login to WHM
2.Select Generate a SSL Certificate & Signing Request under the SSL/TLS Tab in the left side of WHM
3.Provide the correct details.
4.Then click the Create bottom. Now the private key, and CSR will send to the below mention email address (Contact Info)
Please note
For SSL installation the account require dedicated IP and a valid SSL Certificate
Steps to create CSR from WHM
1.Login to WHM
2.Select Generate a SSL Certificate & Signing Request under the SSL/TLS Tab in the left side of WHM
3.Provide the correct details.
4.Then click the Create bottom. Now the private key, and CSR will send to the below mention email address (Contact Info)
Change HTTPD port number
We all know that the default Port number of Apache is 80. For more security purpose we can change Apache port number, Please see below mentioned steps inorder to change the port number.
Assume you need to change the port number of httpd from 80 to 8080 and for https from 443 to 1023
Search the httpd configuration file
#vi /usr/local/apache/conf/httpd.conf
Add multiple Webmail Interfaces in Plesk
Sometimes you may arise a situation that client need to access multiple webmails Applications (such as Horde, SqurrileMail, Roundcube ...) at a time in Plesk, through different links such as webmail.domainname.com for Horde and domainname.com/webmail for SqurrileMail. In such situation you can follow the below mentioned steps.
Please go through the example inorder to solve these type of issues.
At first login to Plesk and go to the Clients control panel
Click on Mail tab as specified in the screen shot.

Now you will be directed to the following page. Click on Change Settings option in the Mail tab.

Multiple PHP versions in the cPanel server
The PHP version on the servers will be the most tested out or proven one. But some clients may want a newer version and make use of the various upcoming features. Due to the various compatibility issues, we can't perform a server wide PHP version change. In such cases, we need to install the newer version with the existing one and enable the client to switch to the newer one by changing the Handler.
Scenario
The client is hosted on a server with php 5.3.24 and he want to enable 5.4.14 for his domain. There are various blogs about running different major version of PHP on the server ie php 5 and php 4. But enabling different minor versions of same major version is a tricky one.
Recompile and install the default PHP (Optional)
If the existing installation is fine and has the necessary modules , then you can skip this step. Otherwise you need to recompile it using
/scripts/easyapache
Once it is done. You can proceed with the new PHP 5.4.14
Wordpress Sample index page
If you face any hack attempts like, may be your your wordpress index page is hacked by the hcaker. You can use below mentioned index page.
===========================================================
<?php
/**
* Front to the WordPress application. This file doesn't do anything, but loads
* wp-blog-header.php which does and tells WordPress to load the theme.
*
* @package WordPress
*/
/**
* Tells WordPress to load the WordPress theme and output it.
*
* @var bool
*/
define('WP_USE_THEMES', true);
/** Loads the WordPress Environment and Template */
require('./wp-blog-header.php');
===============================================================
===========================================================
<?php
/**
* Front to the WordPress application. This file doesn't do anything, but loads
* wp-blog-header.php which does and tells WordPress to load the theme.
*
* @package WordPress
*/
/**
* Tells WordPress to load the WordPress theme and output it.
*
* @var bool
*/
define('WP_USE_THEMES', true);
/** Loads the WordPress Environment and Template */
require('./wp-blog-header.php');
===============================================================
Mysql Commands
Configuration file
/etc/my.cnf /root/.my.cnf
>mysqladmin varialbles
>mysql
>mysql -h <hostname/IP> -u user -p<password> dbname
logs
datadir cPannel-/var/lib/mysql server_name.err
file formats - storage engine format
Create Database
>mysqladmin create dbname;
>mysql> use dbname;
>SELECT User FROM mysql.user;
>mysql> show databases;
>mysql> show tables;
>mysql>CREATE USER 'monty'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'some_pass';
>select user();
Command to change the permissions
Use below mentioned command to change the permissions
For files
find . -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;
For Directories
find . -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;
:)
For files
find . -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;
For Directories
find . -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;
:)
Command to find Symbolic links
Some times we may face hack attempts in the servers. The hackers place may symbolic links in a particular account in order to login to other account also as root user.
In order to find the symbolic links in the server use below mentioned command
#find . -type l -not -xtype l
Exim Getting restarted automatically
Issue:
imap failed @ Mon May 18 10:43:25 2009. A restart was attempted automagically.
Service Check Method: [tcp connect]
Failure Reason: TCP Transaction Log:
> A001 LOGIN
>> __cpanel__service__auth__imap__98iAtd2AmGfa333Whn3ZFBBpX1wI8RSyJpsiPp
>> vfbjKFhkb_bHqULKRGsLqrto0_
>> 8nwcb9SZnQRfvdNcfx6lsZlqWJo8EFlJzu1CBPrwxCE1HY4jNQznoFm7IbgjFPRR
Steps to FIX the issue
/scripts/courierup –force
service courier-imap restart
service courier-authlib restart
Another FIX says
1020 cd /var/cpanel/serviceauth/
1021 ls
1022 rm -rf exim
1023 /etc/rc.d/init.d/cpanel restart
1024 /etc/rc.d/init.d/exim restart
Disable error reporting using .htaccess
Just write below mentioned lines in .htaccess file
php_flag display_startup_errors off
php_flag display_errors off
cPanel Licence Verification
How to check cPanel Licence Verification
To verify the licence of the cPanel open this link http://verify.cpanel.net/. Enter the main public IP address for a server to check if it has a valid cPanel product license.
If the licence is valid then login as root to the server and run the following to refresh the license.
If this command errors or you do not see the server
contacting cPanel license servers to verify your license, please check
that your server is able to contact servers via port 80 (so, check your
firewall's OUTPUT options) and that you have a proper hostname set on
your server. cPanel makes the connection to one of the cPanel licensing
servers through port 2089. So we should make sure that this port is
open.
Some times on running the cpkeyclt command, you will encounter the error given below
To verify the licence of the cPanel open this link http://verify.cpanel.net/. Enter the main public IP address for a server to check if it has a valid cPanel product license.
If the licence is valid then login as root to the server and run the following to refresh the license.
# /usr/local/cpanel/cpkeyclt
Telnetting to cPanel License Server
root@server [~]# telnet auth.cpanel.net 2089Trying 198.66.78.9…Connected to auth.cpanel.net (198.66.78.9).Escape character is ‘^]’.200 cPanel License Service Version 12.0root@server [~]# |
Enable Hotlink Protection
Enable Hotlink Protection
Hot link protection is security measure inorder to prevents other
websites from directly linking to files and pictures on your website.
Other sites will only be able to link to file types that you don't
specify.
Lets check how to enable Hotlink Protection.
1.Login to Cpanel.
2.Select Hotlink Protection under the Security tab.
You will be redirected to the following page.
3.Click on Enable button. Then the hotlink protection will be enabled for that particular domain.
4.Now in the URLs to allow access: box Enter the URL to any domain you wish to allow hotlinking.
5.Provide the extensions in the Block direct access for these extension box.
6.In the Redirect request to this URL: you can enter a URL that anyone trying to hotlink will see in the place of image, etc.
7.Click on Submit button.
| Hotlink Protection – Preventing Bandwidth Theft Bandwidth theft or hotlinking is direct linking to a web site's files such as images,vedios etc, this will result to high bandwidth consumption. For example some would be using an <img> tag to display a JPEG image on his website which is used in your own site. |
Lets check how to enable Hotlink Protection.
Enable Hotlink protection for an account.
Through cPanel1.Login to Cpanel.
2.Select Hotlink Protection under the Security tab.
You will be redirected to the following page.
3.Click on Enable button. Then the hotlink protection will be enabled for that particular domain.
4.Now in the URLs to allow access: box Enter the URL to any domain you wish to allow hotlinking.
5.Provide the extensions in the Block direct access for these extension box.
6.In the Redirect request to this URL: you can enter a URL that anyone trying to hotlink will see in the place of image, etc.
7.Click on Submit button.
ACL ( Access Control Lists )
The Access Control List helps to assign permissions for files and directories for a particular user or group. For example, different permissions cannot be configured for different users and groups normally. Thus, Access Control Lists (ACLs) are used in those cases.
Note :-
The acl package is required to implement ACLs. It contains the utilities used to add, modify and remove ACL information.
Syntax :-
To Set acl for a file:-
# setfacl -m rules file
User:
Eg : # setfacl -m u:user1:rw /root
Group:
Eg : # setfacl -m g:group1:rwx /root
To check the acl permissions of a file:-
# getfacl file
Removing an ACL :-
# setfacl -x rules file
Eg:
# setfacl -x u:user1 /root
WHMCS
Lets look WHMCS in detail
Introduction
WHMCS is an all-in-one client management, billing & support solution for online businesses. Handling everything from signup to termination. It is not limited to just web hosting, any business with a need for online billing, particularly of a recurring nature, for example services or memberships, then WHMCS can be a perfect solution.WHMCS can be used as a standalone client area portal, or integrated into your website, and provides you with a members area to allow clients to signup and manage their account & services with you, make payments, and request support.
WHMCS integrates with payment gateways, server provisioning APIs, domain registrars & fraud protection services to be able to fully automate the ordering and provisioning process.
Billing
Billing is made easy in WHMCS. You can send your clients high quality professional looking invoices with PDF file attached that has new invoice notifications and payment reminder notices. So the clients need not have to login to their client area to view the invoices. Also the invoices are customisable.Features:
- Automated Invoicing will take care of billing your customers on a recurring basis.
- PDF Invoices can be downloaded for saving or printing.
- Automated Payment Processing is offered with all the supported gateways and you can extend it to others by building your own payment processing module.
What is EPP code
EPP Code
Domain authorization code also known as EPP Code provides an extra level of security for the domain name registration. Unique for each domain name and is assigned by the registrar at the time the domain name is registered. it is needed when you would like to transfer domain from one registrar to another.
What is Domain Name Registrar
Domain Name Registrar
Service that allows you to officially register your desired website domain name so that it is unique to you and no one else can own it.
ICANN(Internet Corporation for Assigned Name & Numbers)
ICANN is a private non-gov,non-profit corporation that has been given the responsibility of allocating IP addresses and managing the Domain Name System.
Domain Name System is nothing but typing a website by its name rather than its numerical IP.
Traceroute
How to perform traceroute in different os
In Windows,
Start > Programs > Accessories > Command Prompt.
c:\> tracert <domain.com>
Linux:
get into a terminal and execute the command as given below
$traceroute <domain.com>
MAC
These steps were created using Mac OS X. For earlier operating systems, you will need to download and use a third party program.
1. From your hard-drive, open the Applications folder, and click to open the Utilities folder.
2. Double-click Terminal.
3.Type traceroute followed by your domain name, and hit Enter.
How to check OS versions
For Redhat OS
Like centos ,fedora , debain etc.
#cat /etc/redhat-release
CloudLinux Server release 6.4
For Ubuntu OS
#cat /etc/lsb-release
DISTRIB_ID=Ubuntu
DISTRIB_RELEASE=12.04
DISTRIB_CODENAME=precise
DISTRIB_DESCRIPTION="Ubuntu 12.04.2 LTS"
Like centos ,fedora , debain etc.
#cat /etc/redhat-release
CloudLinux Server release 6.4
For Ubuntu OS
#cat /etc/lsb-release
DISTRIB_ID=Ubuntu
DISTRIB_RELEASE=12.04
DISTRIB_CODENAME=precise
DISTRIB_DESCRIPTION="Ubuntu 12.04.2 LTS"
chattr Command
How to use the chattr command ?
This is an admin command. Only the Root user can change the file attributes/Process. chattr command is used to change the file attributes.
Syntax:
chattr [options] filename
+i - Make the file as Read-Only.
-i - Remove the Read-Only.
+a - Can't open file for writing
-a - Open file for writing.
+S - The changes in the file are written synchronously on the disk.
Example:
chattr +i file.txt
chattr -i file.txt
This is an admin command. Only the Root user can change the file attributes/Process. chattr command is used to change the file attributes.
Syntax:
chattr [options] filename
+i - Make the file as Read-Only.
-i - Remove the Read-Only.
+a - Can't open file for writing
-a - Open file for writing.
+S - The changes in the file are written synchronously on the disk.
Example:
chattr +i file.txt
chattr -i file.txt
/etc/hosts entry
The entries in the /etc/hosts file
You can use below mentioned steps to make changes in the file.
Example :
- If you are using a Windows machine
Add entry in this file : %SystemRoot%\system32\drivers\etc\ (where %SystemRoot% is C:\Windows in a Normal case, change it accordingly)
- If you are using a Linux machine, Add entry here in this file : /etc/hosts
- If you are using a Mac, Add entry here in this file : /private/etc/hosts
<IP> domain.com www.domain.com |
Example :
192.234.45.12 example.com www.example.com
cPanel Log Files
The list of Log files
This will help you for trouble shooting the problems
Instructions
Access log & cpsrvd user activity /usr/local/cpanel/logs/access_
Account transfers & related activity /var/cpanel/logs
Account activity audit log /var/cpanel/accounting.log
Account bandwidth history /var/cpanel/bandwidth
/var/cpanel/bandwidth.cache
Brute force protection (cphulkd) /usr/local/cpanel/logs/
Backup Logs /usr/local/cpanel/logs/
Maldet scan
How to run a Maldet scan in the server
maldet -a -b ~user
tail /usr/local/maldetect/event_log
How to Fix the hits
cd /usr/local/maldetect
&&
rm -rf sigs/ && mkdir sigs/ && maldet -u
Permissions for webhosting accounts
public_html - 750
Folders - 755
CGI and Perl scripts - 755
.html .php and other Document Types - 644
Top command
top command displays the top cpu processes in the server
N-sort tasks by pid (numerically).
A-sort tasks by age (newest first).
P-sort tasks by CPU usage (default).
M-sort tasks by resident memory usage.
T-sort tasks by time / cumulative time.
1-display CPUs seperatly
Command to check DDoS attacks
How to check is there any DDoS attacks to your server?
use the command
netstat -plan|grep :80 |awk '{print $5}' |cut -d: -f1 |sort |uniq -c |sort -n
This will check number of ip connections to the server.
Create a PHP info page
How to Create a PHP info page ?
Create phpinfo.php file under the document root
#vi phpinfo.php
<?
phpinfo();
?>
You can test it by checking the url
domainame/phpifo.php
Difference between TCP and UDP
What is the Difference between TCP and UDP Protocols ?
TCP - Transmission Control Protocol
UDP - User Datagram Protocol
* TCP is connection-oriented protocol. and UDP is connectionless protocol.
* TCP Data is read as a "stream," and in UDP Packets are sent as "Packets" (individually).
* TCP guarantees that will reach the destination. But UDP won't guarantees.
* UDP is faster for sending small amounts of data since no connection setup is required, The data can be sent in less time then it takes for TCP to establish a connection.
DNS propagation delay
What is mean by Propagation delay ?
Lets look close into it:-
When a request to get the IP of a domain is generated from a machine or client, the ISP fetches the information from the authoritative name servers. Then it keeps the records in the ISP cache for a
specified interval of time. This process of keeping the records is called ISP caching.
It can be compared with a browser cache up to a good extent. If another user requests to access the domain
from the same ISP, the IP stored in the cache will be served to the new client. Obviously the speed will be higher. You can experience the difference while accessing google.com and a normal, not so common domain.
Unlike browser cache, we don't have any control over ISP cache and can't delete the cache file. So when a change is done on the authorative DNS servers, to reflect it on all ISPs we need to wait for the refresh interval specified in zone file. This time delay can take up to 48 hours and is called DNS propagation delay.
During this time, there can be difference for the modified records from different ISPs.
Lets look close into it:-
When a request to get the IP of a domain is generated from a machine or client, the ISP fetches the information from the authoritative name servers. Then it keeps the records in the ISP cache for a
specified interval of time. This process of keeping the records is called ISP caching.
It can be compared with a browser cache up to a good extent. If another user requests to access the domain
from the same ISP, the IP stored in the cache will be served to the new client. Obviously the speed will be higher. You can experience the difference while accessing google.com and a normal, not so common domain.
Unlike browser cache, we don't have any control over ISP cache and can't delete the cache file. So when a change is done on the authorative DNS servers, to reflect it on all ISPs we need to wait for the refresh interval specified in zone file. This time delay can take up to 48 hours and is called DNS propagation delay.
During this time, there can be difference for the modified records from different ISPs.
How to Register a Domain
Domain Name Registration
Lets look how to register a Domain:
Domain registration is the process by which a company or individual can procure a domain, such as ww.example.com.
Once you have completed domain registration the domain becomes yours for the period of the contract,
usually one year. Before registration expires it must be renewed, or the domain goes to a new status called Domain Renewal Hold for 15-60 days (dependingon the tld), and even after that period if the domain is not renewed, it will be deleted and will be available to the public for sale.
Domain registration is available to the public via a registrar authorized by ICANN. Fees and services vary from company to company.
Lets look how to register a Domain:
Domain registration is the process by which a company or individual can procure a domain, such as ww.example.com.
Once you have completed domain registration the domain becomes yours for the period of the contract,
usually one year. Before registration expires it must be renewed, or the domain goes to a new status called Domain Renewal Hold for 15-60 days (dependingon the tld), and even after that period if the domain is not renewed, it will be deleted and will be available to the public for sale.
Domain registration is available to the public via a registrar authorized by ICANN. Fees and services vary from company to company.
ICANN
ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers)
The Internet is tightly managed by Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN).
To reach another person on the Internet you have to type an address into your computer - a name or an IP address. That address has to be unique so computers know where to find each other. Coordinates these
unique identifiers across the world. Without that coordination we wouldn't have one global Internet.
ICANN doesn’t control content on the Internet. But through its coordination role of the Internet’s naming system, it does have an important impact on the expansion and evolution of the Internet.
Different Types of TLDs
Generic TLD
TLDs used by particular type of organisation. The given below listed the different types of Generic TLDs.
TLDs used by particular type of organisation. The given below listed the different types of Generic TLDs.
- .aero - for the air transport industry
- .asia - for companies. organisations and individuals in the Asia-Pacific region
- .biz - for business use
- .cat - for Catalan language/culture
- .com - for commercial organizations, but unrestricted
- .coop - for cooperatives
- .edu - for post-secondary educational establishments
- .gov - for governments and their agencies in the United States
- .info - for informational sites, but unrestricted
- .int - for international organizations established by treaty
- .jobs - for employment-related sites
- .mil - for the US military
- .mobi - for sites catering to mobile devices
- .museum - for museums
- .name - for families and individuals
- .net - originally for network infrastructures, now unrestricted
- .org - originally for organizations not clearly falling within the other gTLDs, now unrestricted
- .pro - for certain professions
- .tel - for services involving connections between the telephone network and the Internet
- .travel - for travel agents, airlines, hoteliers, tourism bureaus, etc.
ccTLDs - Country Code TLDs
These Domain is generally reserved or used for country or Tertiary. The given below listed the different types of Country Code TLDs.
What is the domain name system and a short note on ICANN
The domain name system, or, is a system designed to make the Internet accessible globally. The main way computers that make up the Internet find one another is through a series of numbers, with each number (called an “address”) correlating to a different device. However it is difficult for the human mind to remember long lists of numbers so the uses letters rather than numbers, and then links letter strings with a precise series of numbers.
A domain name itself comprises two elements: before and after “the dot”. The part to the right of the dot, such as “com”, “net”, “org” and so on, is known as a “top-level domain” or TLD. One company in each case (called a registry), is in charge of all domains ending with that particular and has access to a full list of
domains directly under that name, as well as the addresses with which those names are associated.
The part before the dot is the domain name that you register and which is then used to provide online systems such as websites, email and so on. These domains are sold by a large number of “registrars”, free to charge whatever they wish.
ICANN draws up contracts with each registry. It also runs an accreditation system for registrars. It is these contracts that provide a consistent and stable environment for the domain name system, and hence the Internet.
ICANN plays a similar administrative role with the addresses used by computers as it does with the domain names used by humans. In the same way that you cannot have two domain names the same (otherwise you never know where you would end up), for the same reason it is also not possible for there to be two IP addresses the same.
It co-ordinate how addresses are supplied to avoid repetition or clashes. . ICANN is also the central repository for addresses, from which ranges are supplied to regional registries who in turn distribute
them to network providers.
Root servers
Lets see what is mean by Root Servers
They are part of the Domain Name System (DNS).
The root zone file describes where the authoritative servers for the DNS top-level domains (TLD) are located; in other words: which server one has to ask for names ending in one of TLDs, such as ORG, NET, NL or AU.
There are 13 root servers at present – or, more accurately, there are 13 addresses on the Internet where root servers can be found (the servers that have one of the 13 addresses can be in dozens of different physical locations).
These servers all stores a copy of the same file which lists an address for each top-level domain (.com, .de, etc) where that registry’s own address book can be found.
For more details visit :-
http://linuxtric.blogspot.in/2013/02/root-name-servers.html
They are part of the Domain Name System (DNS).
The root zone file describes where the authoritative servers for the DNS top-level domains (TLD) are located; in other words: which server one has to ask for names ending in one of TLDs, such as ORG, NET, NL or AU.
There are 13 root servers at present – or, more accurately, there are 13 addresses on the Internet where root servers can be found (the servers that have one of the 13 addresses can be in dozens of different physical locations).
These servers all stores a copy of the same file which lists an address for each top-level domain (.com, .de, etc) where that registry’s own address book can be found.
For more details visit :-
http://linuxtric.blogspot.in/2013/02/root-name-servers.html
TLD (Top Level Domain)
What is mean by TLD?
TLD means Top Level Domain.
Domain extension on the Internet are often called as TLDs(Top Level Domains). Its something you encountered every time while you surfing the web page.
In short TLDs are the last part of the domain name. For example .com, .net , .org etc..
There are 2 types are TLDs.They are
* Generic TLD &
* ccTLD Country code Top Level Domain
TLD means Top Level Domain.
Domain extension on the Internet are often called as TLDs(Top Level Domains). Its something you encountered every time while you surfing the web page.
In short TLDs are the last part of the domain name. For example .com, .net , .org etc..
There are 2 types are TLDs.They are
* Generic TLD &
* ccTLD Country code Top Level Domain
How to unblock an IP from the server
Lets see how to unblock an IP from the server Firewall
At first grep the IP whether it is blocked in the server or not
#csf -g <IPaddress>
If this query shows that the IP is blocked in the server, Then unblock the IP from the server using the below command
#csf -dr <IPaddress>
It will drop the IP from the server.
At first grep the IP whether it is blocked in the server or not
#csf -g <IPaddress>
If this query shows that the IP is blocked in the server, Then unblock the IP from the server using the below command
#csf -dr <IPaddress>
It will drop the IP from the server.
How to enable Port number ?
How to enable TCP Port number?
How to enable UDP Port number?
Lets see how to enable incoming and outgoing TCP & UDP Ports in Linux / Unix Servers
Edit the configuration file
#vim /etc/csf/csf.conf
Add the necessary ports in the TCP incoming and outgoing & UDP incoming & outgoing line specified in the configuration file.
Now restart the service
#service csf restart
#csf -r
#csf -e
How to enable UDP Port number?
Lets see how to enable incoming and outgoing TCP & UDP Ports in Linux / Unix Servers
Edit the configuration file
#vim /etc/csf/csf.conf
Add the necessary ports in the TCP incoming and outgoing & UDP incoming & outgoing line specified in the configuration file.
Now restart the service
#service csf restart
#csf -r
#csf -e
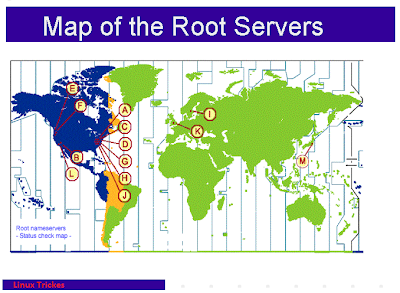
Root Name Servers
13 Root Name servers
There are 13 Root Name servers are situated around the world. As the picture shown above Root name servers starts from Capital letter A to M.
10 servers were originally in the United States , Some are now operated via any-cast.
3 Servers were originally in Stockholm(I), Amsterdam(K) and Tokyo(M)
There are 13 Root Name servers are situated around the world. As the picture shown above Root name servers starts from Capital letter A to M.
10 servers were originally in the United States , Some are now operated via any-cast.
3 Servers were originally in Stockholm(I), Amsterdam(K) and Tokyo(M)
How the DNS works ?
Working Overview of DNS
Lets look the working overview of DNS
The basic function of DNS is to resolve IP address from domain name. We must know the basics of
DNS before proceeding further
Suppose, you are searching the domain http://www.example.com in your browser,
The first step is that the query checks to which file or service it should search for the IP address. The order is
specified in /etc/nsswitch.conf.
There the entry will be specified as like
************
hosts: files dns
************
Which means, for programs that want to resolve an address. They should use the files present in the
system (E.g./etc/hosts,) first, and then DNS servers.
In our case it will first check for the IP address of example.com in the /etc/hosts file and if it fails to find it, then it will check for DNS.
The resolver library used by BIND needs a configuration file which specifies the name servers and it is /etc/resolv.conf. If this file does not exist or is empty, the resolver assumes the name server is on your local host.
Lets look the working overview of DNS
The basic function of DNS is to resolve IP address from domain name. We must know the basics of
DNS before proceeding further
Suppose, you are searching the domain http://www.example.com in your browser,
The first step is that the query checks to which file or service it should search for the IP address. The order is
specified in /etc/nsswitch.conf.
There the entry will be specified as like
************
hosts: files dns
************
Which means, for programs that want to resolve an address. They should use the files present in the
system (E.g./etc/hosts,) first, and then DNS servers.
In our case it will first check for the IP address of example.com in the /etc/hosts file and if it fails to find it, then it will check for DNS.
The resolver library used by BIND needs a configuration file which specifies the name servers and it is /etc/resolv.conf. If this file does not exist or is empty, the resolver assumes the name server is on your local host.
DNS
What is mean by DNS ?
The DNS is considered as the most essential service in the case of a website.
Its failure results webserver, Mail server, mysql service for a website to be seen down. So understanding the DNS is essential to work as a Sysadmin.
The first step regarding a domain is registering a domain name with the registrar. Then two name
servers will be assigned for the domain.
Once the Name servers are assigned, it implies that the valid records for DNS of the domain are present in the specified Name Servers. It means that the changes made in these NS records alone will be valid and propagated through the Internet. Hence these name servers are termed as "authoritative Name servers".
The DNS is considered as the most essential service in the case of a website.
Its failure results webserver, Mail server, mysql service for a website to be seen down. So understanding the DNS is essential to work as a Sysadmin.
The first step regarding a domain is registering a domain name with the registrar. Then two name
servers will be assigned for the domain.
Once the Name servers are assigned, it implies that the valid records for DNS of the domain are present in the specified Name Servers. It means that the changes made in these NS records alone will be valid and propagated through the Internet. Hence these name servers are termed as "authoritative Name servers".
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)